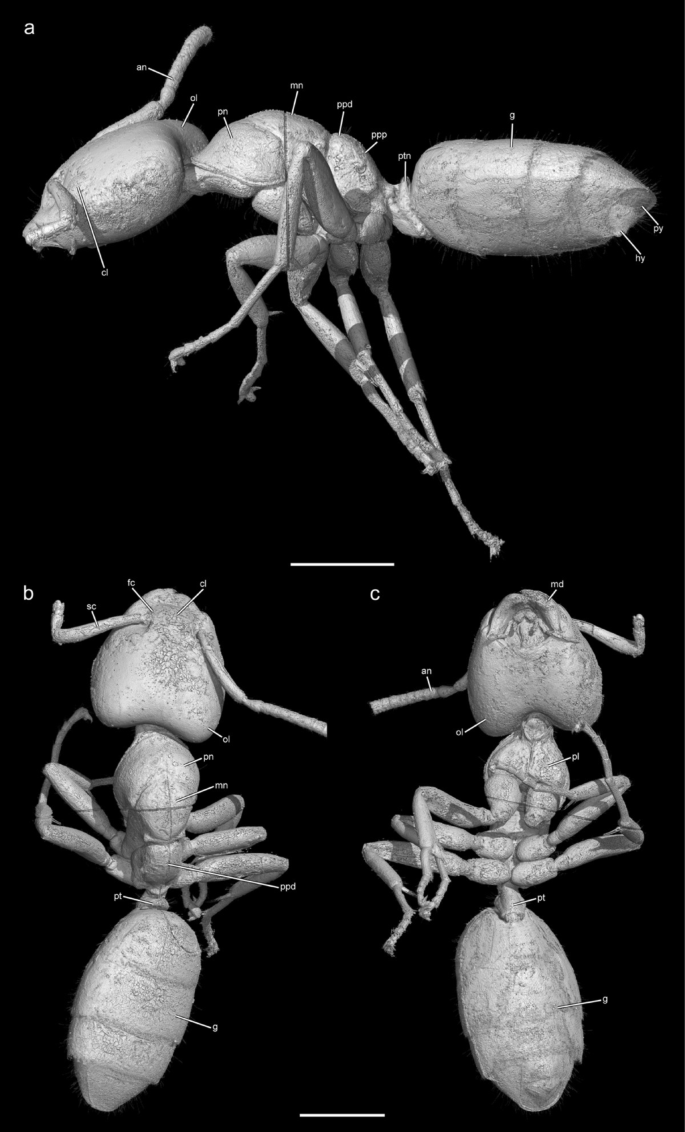
iGEM Hamburg Team Awarded Gold Medal
| With their project “DeathCapTrap,” the iGEM Hamburg team developed an antidote to one of the most dangerous fungal toxins in the world. They were awarded a gold medal for their work at the largest student competition for synthetic biology in Paris. The Hamburg team of ten students was received a gold medal and another nomination at this year's iGEM Grand Jamboree, the synthetic biology industry’s largest innovation event hosted by the International Genetically Engineered Machine (iGEM) Foundation. This placed the team among the top three project groups in their category. A total of 420 teams from more than 50 countries participated in the competition. Congratulations to the team! We are glad that we could support the effort a tiny bit with the Maxwell cluster. See also the
|  |